
Part.1
introductory


Payment methods play a key role in consumers' shopping experience and purchase decisions in them (Xu, Bai, & Wan, 2017). However, little is known about its underlying neural basis. In this study, we combined event-related potentials (ERPs), a neuroscientific technique with the advantage of measuring implicit psychological variables to reveal the mechanisms behind behaviors, with an online shopping task to reveal the differences in consumers' perceptions of online payment and cash-on-delivery in different shopping contexts.
Part.2
Method


Tested:
There were 18 males and 11 females aged between 18 and 27 (M=22.724, SD=2.644) years.
Material:
Mice, ballpoint pens, expansion sockets, storage boxes and USB drives are considered as search goods (goods whose quality can be known by consumers through their own inspection prior to purchasing the goods), and shampoos, shower gels, sunglasses, pillows and air fresheners are considered as empirical products (goods whose quality can be known only after consuming the goods).
Program:
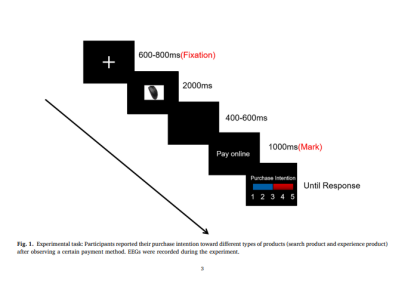
Before the experiment began, participants were briefed about online shopping and how the experiment was conducted. After they fully understood the process, they began the formal experiment and were given feedback on their purchase intentions by tapping on the keyboard. The experiment was divided into 4 blocks of 40 experiments each, and the duration of the experiment was approximately 30 min. The formal experiment process is shown in Figure 1.

Part.3
Results


1. willingness to buy is greater for search goods than for experience goods, p = 0.015. willingness to buy is greater for online payment than for cash on delivery, p = 0.006.
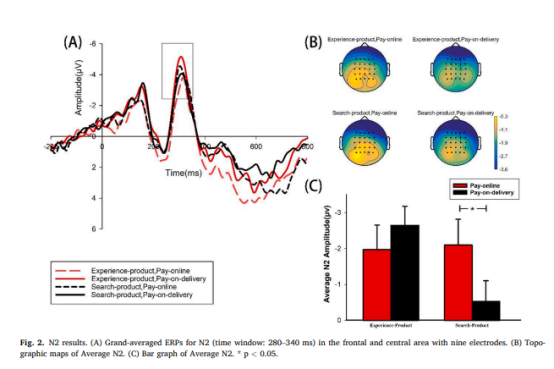
2, the type of goods and the payment method jointly affect the N2 mean amplitude, and there is a significant difference in the N2 mean amplitude induced by the two payment methods when purchasing the searching goods, p = 0.025, with higher N2 mean amplitude induced by online payment. However, there was no significant difference between the two when purchasing experience goods, see Figure 2.


seek2


Part.4
talk over


Differences in the interactions between product type and payment method on the effects of purchase intention and N2 amplitude suggest that in the early cognitive process stage of neural rapid response, subjects mainly perceive risk, which leads to a greater N2 for online payment, but does not directly affect purchase intention. The present study reveals the neurophysiological basis of the effect of product type and payment method on consumers' purchase intention, which is characterized by higher perceived risk and less negative emotions when purchasing the searched product compared to cash on delivery, as indicated by enhanced N2 amplitude and reduced P3 amplitude. This effect disappears with the purchase of the experienced product.
Part.5
Conclusion


This study reveals the neurophysiological basis of the effect of product type and payment method on consumers' willingness to buy, which is characterized by higher perceived risk and less negative emotions when purchasing search goods compared to cash on delivery, as indicated by enhanced N2 amplitude and reduced P3 amplitude. This effect disappears with the purchase of the experienced product.
Part.6
References




Company Profile
This article comes from the WeChat public number: EVERLOYAL






































