


Part.1
Background

Previous articles on fNIRS technology in the aerospace field have focused on introducing you to the assessment of the brain load of air traffic controllers. In this issue, we will take a closer look at the application of portable near infrared (fNIR) in this type of research from the perspective of professional skill development for novice pilots. NIR spectroscopy is often used in real or simulated research environments because of its safety, portability, user-friendliness, and high spatial resolution, as in the case of assessing the skill development of novice pilots.
There is a large body of previous research on the development of specialized skills that suggests that as specialized knowledge and skills are practiced, activation in brain regions responsible for attention and control decreases (Ericsson, 2006; Kelly & Garavan, 2005;), and that this decrease is thought to be a contraction of neural representations of the stimulus (Poldrack, 2000), which frees up some of the cognitive resources to attend to other external afferent stimuli or respond to other task demands (Milton et al., 2004). Measuring activation of attentional and control brain regions associated with task performance can provide a professional level and objective indicator of the degree of development of novice pilot expertise.
Part.2
Method


2.1 Participants
Seven novice pilots between the ages of 21 and 28 with no flight experience participated in the study, one participant was disqualified due to lack of ability to perform basic flight tasks, and all participants signed an informed consent form prior to the study.
2.2 Experiment content
Participants practiced approach and landing tasks in a flight simulator. The turn-around approach task involves the pilot flying over several set waypoints during the approach.as shown in Figure 1The landing mission is carried out by the pilot. For landing missions, the pilot performs the actual landing missionas shown2. In both scenarios, subjects were told to fly as smoothly as possible, learn the optimal path, cope with side winds, and complete the task within certain speed and tilt angle constraints.



seek1


seek2
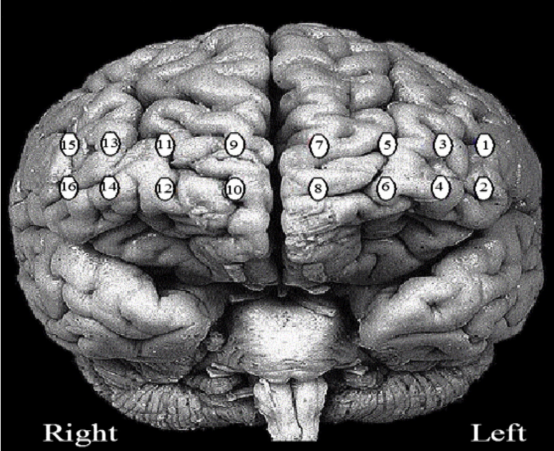


seek3
Part.3
Results


3.1 Self-reported results
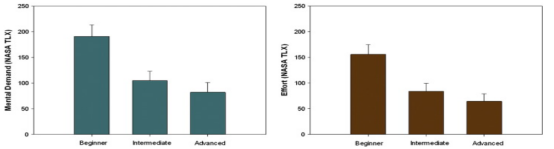
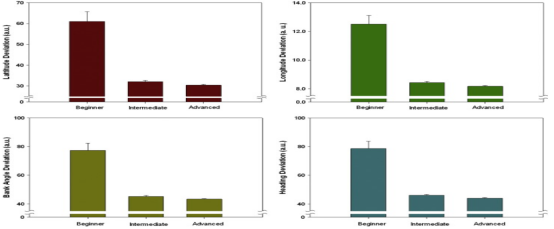
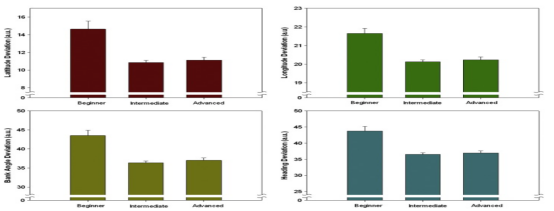
The results of the NASA TLX Index for the UAV task were analyzed using a one-way repeated measures ANOVA. Results indicated significant main effects of practice level (beginner/intermediate/advanced stage) on mental demand and perceived effort. There was a monotonically decreasing trend in both mental demand and perceived effort from the beginner to the advanced stage.Tukey post hoc tests showed that mental demand was significantly higher in the beginner stage than in the other conditions, and the effort results indicated that the beginner stage required a higher level of effort than the other conditions, theAs in Figure 4.

seek4

seek5

seek6
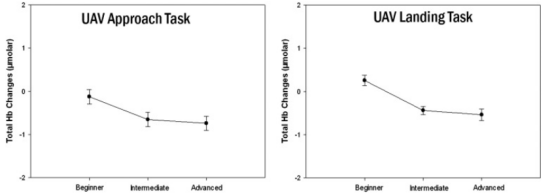

seek7
Part.4
talk over


For both the approach and landing tasks, there were reductions in fNIR measures that were significantly different in level and matched the same trends reported in behavioral performance and self-report measures. Practice and the development of specialized knowledge or skills typically involve reduced activation of attention and control regions, thereby releasing these neural resources to attend to other incoming stimuli or task demands. Measuring activation of these attention and control regions relative to task performance can therefore provide a level of expertise and an objective indicator that differences in prefrontal cortex activation of attention and control regions may also indicate neuroplasticity as a function of task-specific practice. In conclusion, fNIR is a portable, safe, and affordable noninvasive optical brain monitoring technique that can be used to measure hemodynamic changes in the prefrontal cortex.
Part.5
Conclusion


This study provides important information about fNIRS measures of dorsolateral PFC hemodynamic responses and their relationship to mental load, expertise, and performance in a complex multitask environment. The level of expertise does seem to influence the hemodynamic response profile of the left dorsolateral PFC during complex approach and landing tasks.
Part.6
References


1. Hasan Ayaz, Patricia A. Shewokis, Scott Bunce, Kurtulus Izzetoglu, Ben Willems, Banu Onaral,Optical brain monitoring for operator training and mental workload assessment, NeuroImage, Volume 59, Issue 1, 2012, Pages 36-47, ISSN 1053-8119,.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.023.
2. Ericsson, K. A., Hoffman, R. R., Kozbelt, A., & Williams, A. M. (Eds.). (2018). The Cambridge handbook of expertise and expert performance. Cambridge University Press.
3. Kelly, A. C., & Garavan, H. (2005). Human functional neuroimaging of brain changes associated with practice. Cerebral cortex, 15(8), 1089-1102.
https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhi005
4. Milton, J. G., Small, S. S., & Solodkin, A. (2004).On the Road to Automatic: Dynamic Aspects in the Development of Expertise. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology, 21(3), 134-143. doi:10.1097/00004691-200405000-00002
5. Poldrack, R. A. (2000). Imaging brain plasticity: conceptual and methodological issues-a theoretical review. Neuroimage, 12(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2000.0596




Company Profile




This article comes from the WeChat public number: EVERLOYAL






































