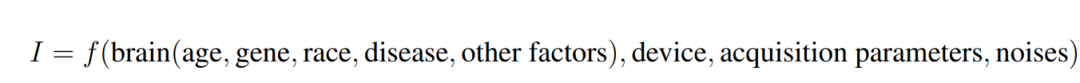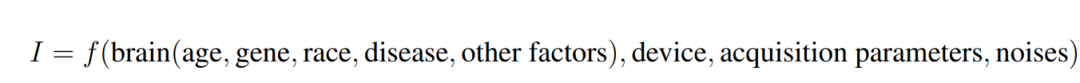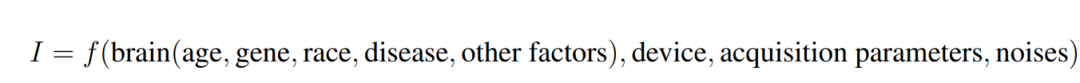The basic principles of NIR have been explained in detail in previous tweets. For a better understanding of this article, here we briefly review the principles of NIR here.
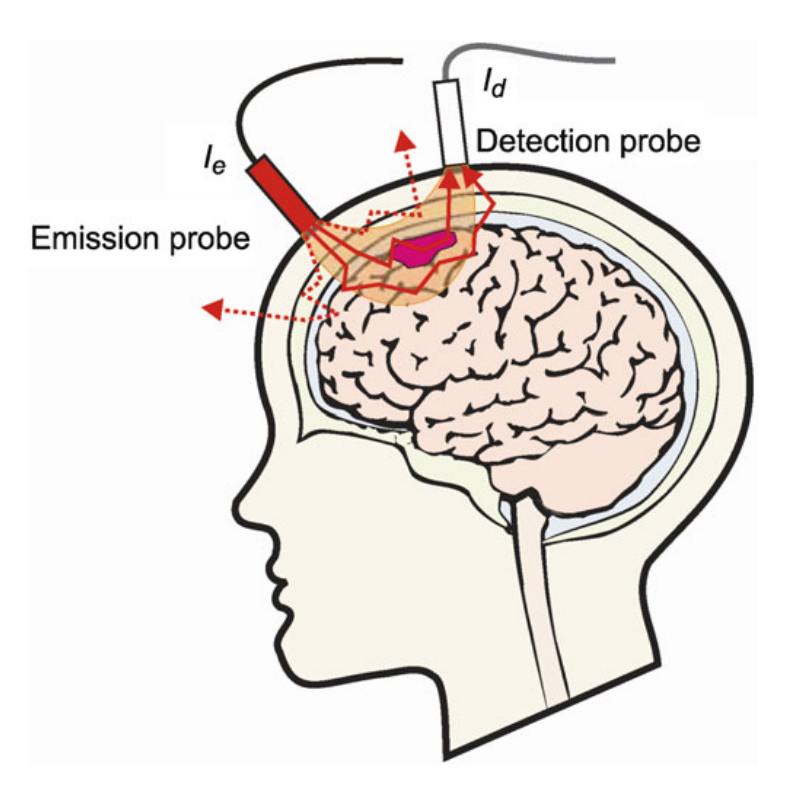
Functional near-infrared spectroscopy is a non-invasive method of measuring brain activity. Since oxygenated hemoglobin (HbO) and deoxyhemoglobin (HbR) have different absorption spectral frequencies, changes in the concentration of HbO and HbR can be determined from near-infrared (NIR) light (wavelengths typically 650 - 950 nm) measurements (Ferrari & Quaresima, 2012; Scholkmann et al. 2014). When the range of the light source and detector is around 3 cm. NIR light can penetrate 1-1.5 cm into the cerebral cortex, which researchers can use to study neurological processes in the brain (Fukui et al., 2003).
Near-infrared photon penetration mode
Principles of Near Infrared Technology
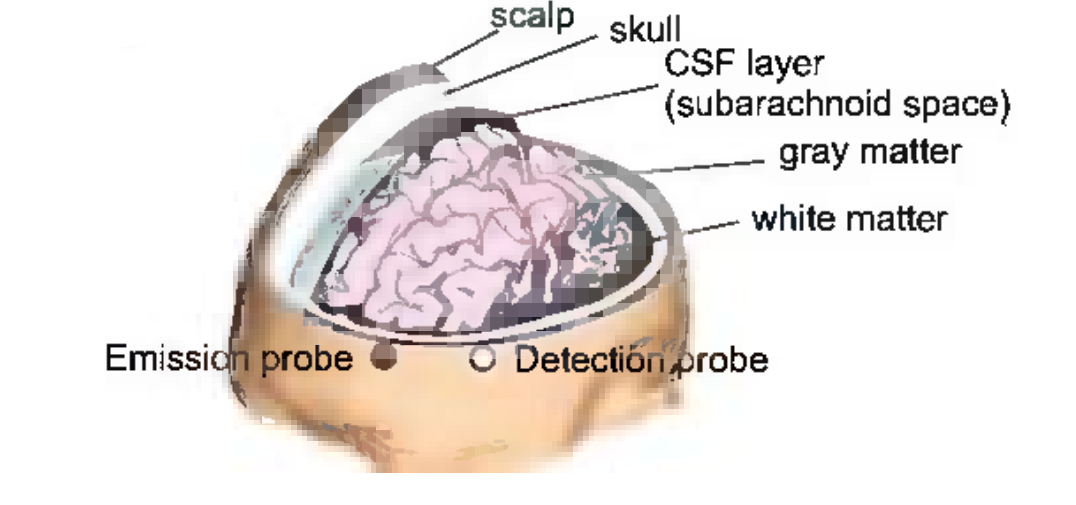
The brain consists of various tissues with different optical properties, and NIR technology is in principle designed to respond to changes in cerebral blood oxygenation by detecting changes in incoming and outgoing light, so it is necessary to study the effect of optical inhomogeneity of the head on the propagation of light through the brain (Jue & Masuda, 2013).
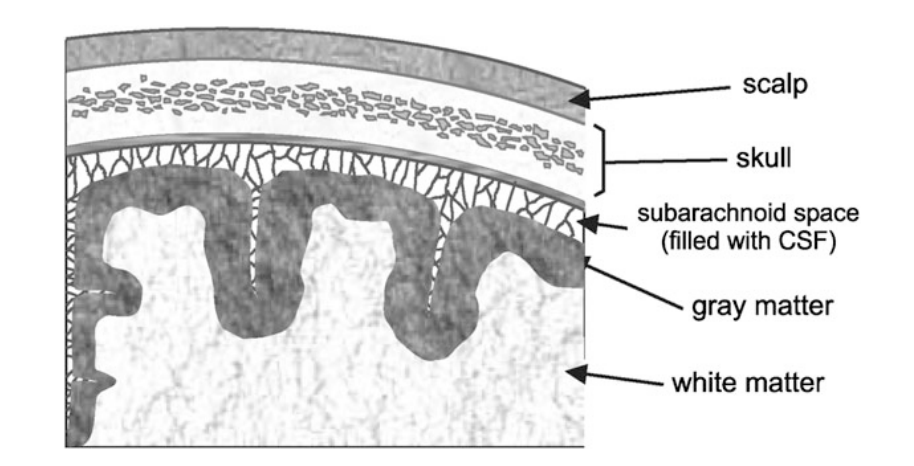
A cross-section of the adult head is shown in the figure. The human brain is a layered structure that is composed of the scalp, skull, dura mater, arachnoid membrane, subarachnoid space filled with cerebrospinal fluid, dura mater, gray matter and white matter. The thickness of the scalp and skull in the brain is uneven, and the surface of the brain is folded with sulci. All of these complex structures have an effect on photon migration in the brain (Jue & Masuda, 2013).
Noise in the near infrared
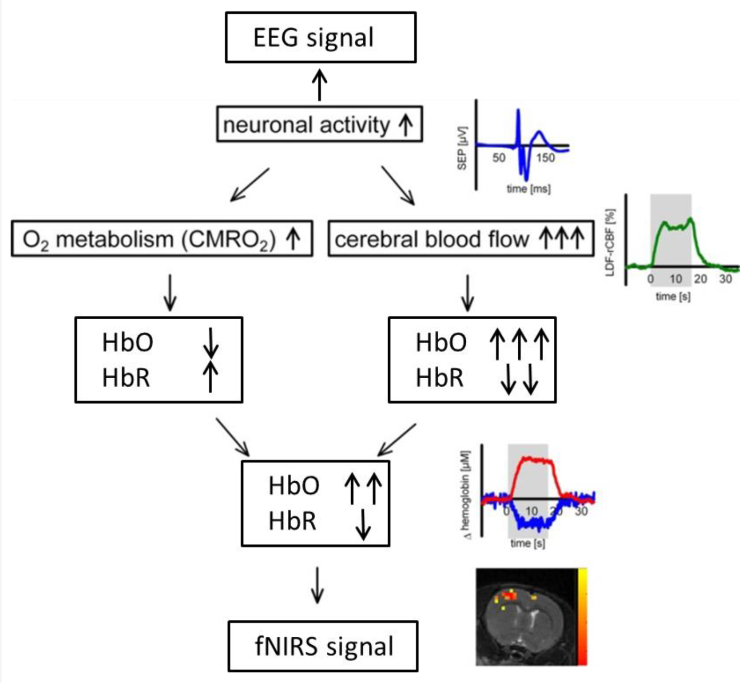
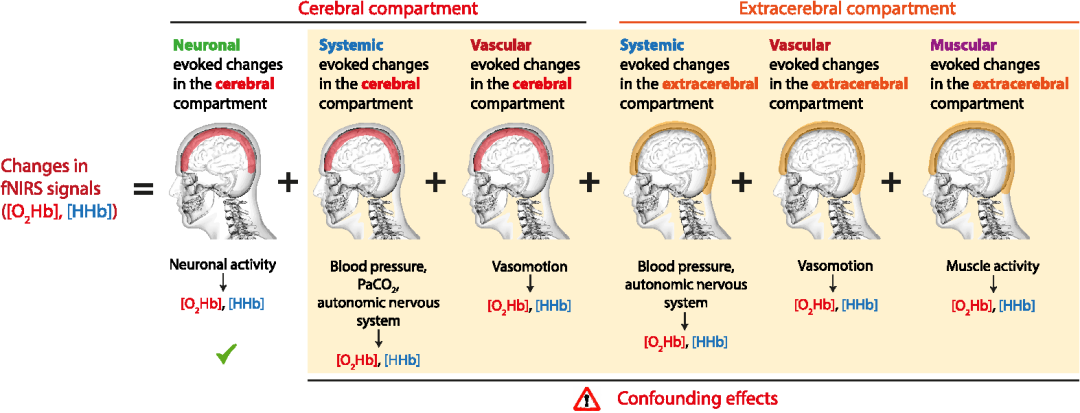
In NIR data acquisition, NIR data can be written as the following equation. This mathematical model emphasizes two important facts:First the neural data is a mixture of different components introduced by the brain, the equipment, the acquisition parameters, and different noises; (and second changes in the brain may be caused by age, genes, ethnicity, disease, and other factors (e.g., stimuli, lifestyle, or environmental factors). And in short time acquisition, even with the same equipment, the interference of machine noise is greater than the physiological signals that are intended to be detected. Therefore, a deeper understanding of noise is not only beneficial for us to recognize it, but also helps us to better understand the nature of neural signals (Scholkmann et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2023).
near-redExternal data modeling formulas
Near-infrared signal composition
Chaddad, A. (2014). Brain Function Diagnosis Enhanced Using Denoised fNIRS Raw Signals. Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering, 07(04), 218-227.
Fernandez Rojas, R., Huang, X., Hernandez-Juarez, J., & Ou, K.-L. (2017). Physiological fluctuations show frequency-specific networks in fNIRS signals during resting state. 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2550-2553.
Ferrari, M., & Quaresima, V. (2012). A brief review on the history of human functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) development and fields of application. NeuroImage, 63(2), 921 -935.
Fukui, Y., Ajichi, Y., & Okada, E. (2003). Monte Carlo prediction of near-infrared light propagation in realistic adult and neonatal head models. Applied Optics, 42(16), 2881.
Jue, T., & Masuda, K. (Eds.). (2013). Application of near infrared spectroscopy in biomedicine. springer.
Lee, G., Lee, S. H., Sang, H. J., & An, J. (2017). Baseline drift detection index using wavelet transform analysis for fNIRS signal. 2017 5th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), 73-76.
Rojas, R. F. (n.d.). Development of an Objective Pain Assessment using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Machine Learning.
Scholkmann, F., Kleiser, S., Metz, A. J., Zimmermann, R., Mata Pavia, J., Wolf, U., & Wolf, M. (2014). A review on continuous wave functional near-infrared spectroscopy and imaging instrumentation and methodology. NeuroImage, 85, 6-27.
Scholkmann, F., Tachtsidis, I., Wolf, M., & Wolf, U. (2022). Systemic physiology augmented functional near-infrared spectroscopy: a powerful approach to study the embodied human brain. Neurophotonics, 9(03).
Zhu, H., Li, T., & Zhao, B. (2023). Statistical Learning Methods for Neuroimaging Data Analysis with Applications. Annual Review of Biomedical Data Science, 6(1), annurev-biodatasci- 020722-100353.
Beijing Everloyal technology co., LTDIt is a new type of high-tech enterprise based on psychological human factors, driving human factors, biomechanics, user experience, virtual reality and other directions, integrating production, research and development, sales and technical services, and has been successfully selected for the list of high-tech enterprises in Zhongguancun.
The driving human factors system, virtual reality graphical editing software, light environment psychological assessment system and psychological and human factors experimental teaching system developed by Hengzhi Technology have entered the domestic market.
As the sole agent of Poland Cortivision NIR, Russia Mitsar EEG in China, the sole agent of Italy BTS surface EMG and other biomechanical and gait analysis products in China, and the sole agent of Netherlands Noldus Behavioral Science, Sweden Tobii Eye Motion Instrument, Netherlands MindMedia Physiology and Biofeedback, US Biopac Physiology, US ETT The domestic licensed agent of products such as olfactory/taste stimulator. The high-tech products operated have served the top universities and the highest level of scientific research units in China, including Tsinghua University, Beijing Normal University, Northeast Normal University, Yanshan University, Qiyuan Laboratory, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen University of Technology, Xi'an University of Science and Technology, Shanghai University, the Second Institute of Aerospace, 27 and 28 of China Electronics Technology Group, while providing technical support for ink Netease, Huawei technology to provide technical support, in the field of talent training, scientific research cooperation, transformation of results and other scientific and technological areas of continuous in-depth cooperation.
This article comes from the WeChat public number: EVERLOYAL