


introductory
Coal miners often work in hot and humid environments, which affects their cognitive functioning, especially working memory. Studies have shown that high temperatures and high humidity reduce miners' reaction time and working memory capacity, and increase workplace risk. Understanding how these environmental factors affect the neural mechanisms of working memory is essential to improve miners' working conditions and enhance operational safety. In this study, we used the fNIRS technique in conjunction with a short-term visual memory task to assess the effects of high temperature and high humidity on miners' working memory, with the aim of optimizing the miners' working environment and improving work efficiency and safety.
01
Experimental background
Coal mine employees often work in hot and humid environments, which adversely affects their health, safety competence, and cognitive functions, especially working memory. Traditional studies have focused on neurophysiological parameters, and the effects of hot and humid environments on cognitive function have been less well studied and have not considered heat and humidity as separate factors. Neuroimaging can reveal links between neural activity and medium- and long-term, ecologically valid outcomes in laboratory settings. fNIRS measures actual brain activity in natural environments and is suitable for studying cognitive processes.
02
Experiment content
01
subject's choice
One hundred coal miners from Hongliulin Mining Group were randomly divided into four groups of 25 each. The participants were all right-handed, had no smoking or drinking habit, had normal vision, and had ensured sufficient sleep before the experiment, had not taken psychotropic drugs, and had signed an informed consent form.
02
experimental condition
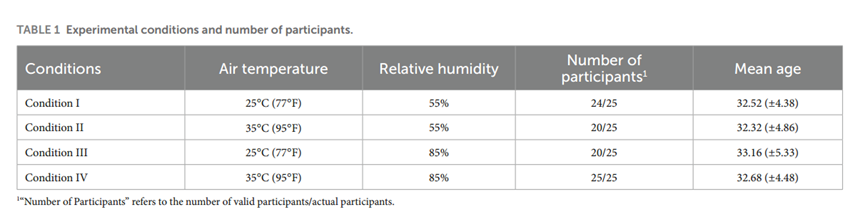
The experiments were conducted in the temperature and humidity chamber of the Safety and Emergency Management Laboratory of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, with the chamber dimensions of 3m*2.4m*4m and external dimensions of 3.2m*2.7m*5.6m, with the temperature setting range of -20°C+90°C and the humidity control range of 20%-95%R.H. The temperature was set at -20°C+90°C and the humidity control range was 20%-95%R.



According to the actual temperature and humidity conditions in Chinese coal mines and the maximum working environment parameters supported by the experimental equipment, the following four experimental environment conditions were set:


03
Experimental design
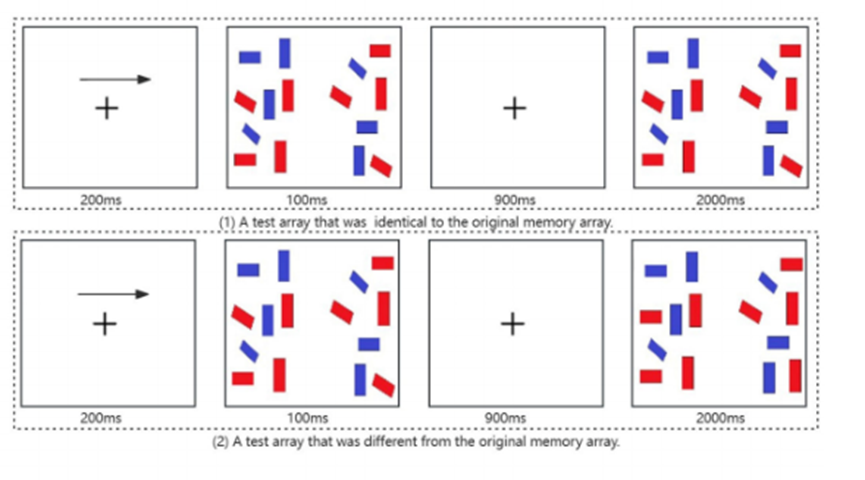
short-term visual memory task: The task was used to study working memory by calculating a model to obtain the working memory capacity (K) based on the hit rate (h) and false alarm rate (f), and recording the reaction time and working memory capacity of the miners under different humidity and temperature conditions in order to explore the working memory performance.


04
experimental procedure
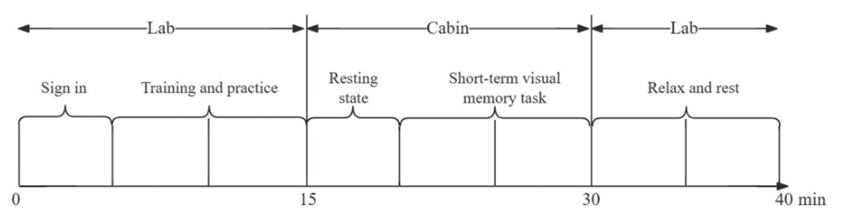
The experiment was conducted from June through August 2023 using the E-Prime 3.0 software to program a short-term visual memory task. Participants arrived at the laboratory, completed a check-in, received an explanation of the experimental procedures, trained and practiced on the task, and then entered the chamber to perform a 10-minute short-term visual memory task consisting of ~180 judgments under specific temperature and humidity conditions while brain activity was recorded using the fNIRS device. After completion of the task, rest and recovery were performed in a room temperature and humidity environment.


04
data acquisition
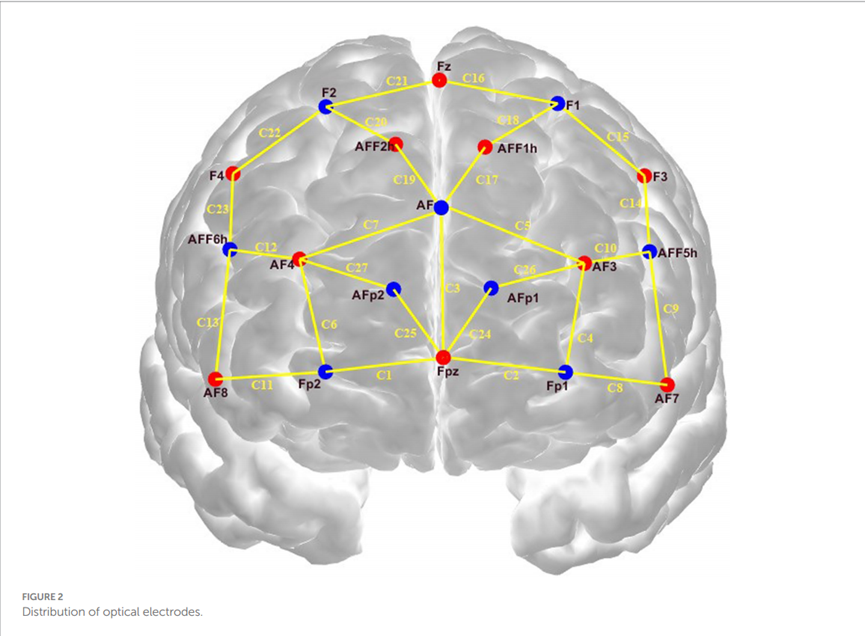
During the resting state and the short-term visual memory task, fNIRS data were acquired using a Cortivision Photon Cap (model C20) and a Cortivision PathFinder, which utilizes a "10-5 system" of electrode placement covering a total of 27 channels near the prefrontal cortex, including 10 light sources and 9 detectors. The device uses a "10-5 system" for electrode placement, covering a total of 27 channels in the vicinity of the prefrontal cortex, including 10 light sources and 9 detectors, with a sampling rate of 5-6 Hz..


05
data processing
After excluding abnormal data, Tukey's HSD was used to compare the reaction time and working memory capacity of subjects under the four conditions, multiple linear regression was used to analyze the effects of temperature and humidity on reaction time and working memory capacity, NIRS_KIT software was used to preprocess the data, and GLM was used to perform the statistical analysis at the individual level, and different region of interest (ROI) β-values and plotted activation maps, compared the changes in Oxy-Hb concentration under different conditions by Tukey's HSD test, investigated the effects of temperature and humidity on Oxy-Hb concentration in miners using multiple linear regression modeling, and analyzed the independent effects of age on Oxy-Hb concentration using ANCOVA, and analyzed the effects of age on Oxy-Hb concentration using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test to compare differences in response to stimuli across conditions across the three ROIs.
06
Results



Behavioral outcomes
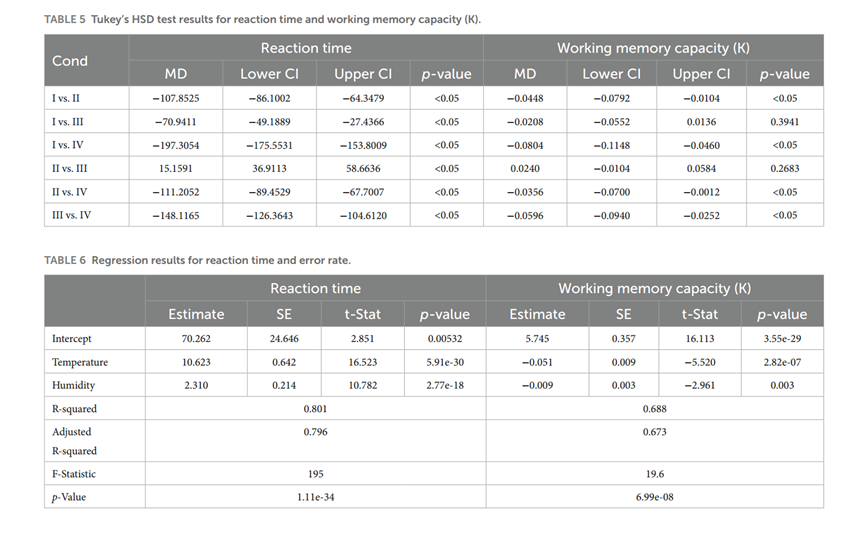


response time (technology): The reaction time for condition I was significantly faster than the other conditions, with temperature and humidity having a significant effect on the reaction time, with an estimated increase of 10.623 units for every 1 degree Celsius increase in temperature and 2.3107 units for every 1 percentage point increase in humidity.
Working memory capacity: The working memory capacity of condition I was significantly higher than that of conditions II and IV. Temperature had a negative effect on the working memory capacity, decreasing the working memory capacity coefficient by 0.05134 for every 1 degree Celsius increase, and decreasing the working memory capacity coefficient by 0.00918 for every 1 percentage point increase in humidity.



NIRS results
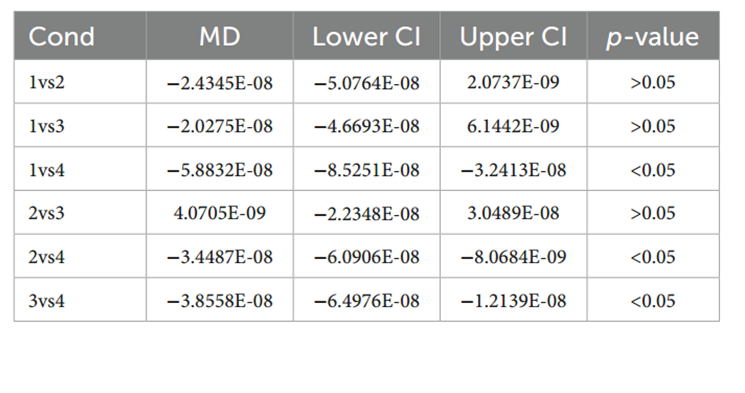





Oxy-Hb concentration: Oxy-Hb concentration was significantly lower in Condition I compared to Condition IV; Condition II was significantly lower in Condition IV compared to Condition IV; Condition III was also significantly lower in Condition IV compared to Condition IV. Temperature and humidity had a significant effect on Oxy-Hb concentration, with a temperature coefficient of 0.315, and an expected increase in oxygen concentration of 0.3145 units for every 1 degree Celsius increase; and a humidity coefficient of 0.0913, and an expected increase in oxygen concentration of 0.0913 units for every 1 percentage point increase, with a greater effect of temperature than of humidity on Oxy-Hb concentration.



ROI activation
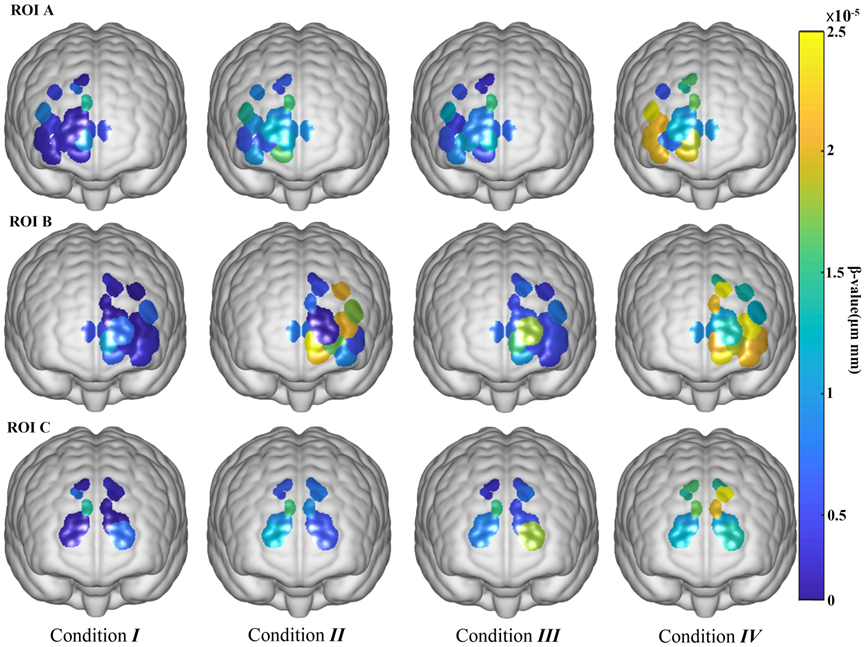


Activation in ROIs A and B (prefrontal cortex) increased with temperature and humidity, and ROI C (supplementary motor area) was less sensitive to temperature. Across all ROIs, temperature and humidity had significant effects on channel activation, with temperature having a more pronounced effect.



talk over
Behavioral data indicated that high temperature and high humidity conditions (Condition IV) were detrimental to miners' cognitive performance, with temperature having a more significant effect on reaction time and error rate than humidity, which is consistent with other findings.
The fNIRS data show that Oxy - Hb concentrations are significantly different under high temperature and high humidity conditions, and that temperature and humidity have a significant effect on Oxy - Hb concentrations, with temperature having a greater effect.
ROI analyses showed that activation of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) is related to cognitive processes, information processing and decision making, and that high temperature and humidity lead to increased cognitive load and task difficulty, thus affecting cognitive task performance. The supplementary motor area (SMA) is mainly involved in the initiation and execution of movement, and the activation of the SMA is relatively low because the short-term visual memory task does not involve complex motor planning and coordination.
summarize
This comprehensive study highlights the urgent need to optimize environmental conditions to improve cognitive abilities and brain function. The findings show that shorter reaction times and improved working memory capacity were significantly associated with cooler, less humid environments (Condition I), highlighting the deleterious effects of heat and humidity on these cognitive functions. In addition, the different activation patterns observed in different brain regions further elucidated the complex interactions between environmental factors and brain activity, with the most extreme conditions (Condition IV) significantly affecting brain function. This study suggests that temperature has a greater impact on cognitive performance than humidity, a key consideration in designing workplaces or environments with high cognitive demands. The implications of these findings go beyond the immediate research context and provide valuable insights into the fields of occupational health, workplace safety, and environmental psychology more broadly.
Original Message
Author: Chenning Tian, Hongxia Li, Shuicheng Tian, Fangyuan Tian and Hailan Yang.
Subject: The neurocognitive mechanism linking temperature and humidity with miners' working memory: an fNIRS study
Crossref DOI link: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2024.1414679
Cortivision Wireless Portable Near Infrared Optical Brain Imaging System
![]()
![]()


The PHOTON CAP device developed by Cortivision is a wireless portable near-infrared brain optical brain imaging system (fNIRS), which is a device that can effectively measure changes in the concentration of hemoglobin in the brain. The device records and analyzes changes in oxyhemoglobin concentration and deoxyhemoglobin concentration in active brain regions during the perception of external stimuli, and speculates on the interrelationships between perceptually active brain regions and their associated brain regions.
The Cortivision PHOTON CAP is a 37-channel device consisting of 16 transmitters (including 4 shortwave transmitters), 10 detectors. The device is wireless, portable, lightweight, safe and highly compatible, and can be used in conjunction with a wide range of devices such as VR, EEG/ERP, oculomotor, and physiological multidetector.






-
Real-time fNIRS and IMU raw data, oxyhemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin, and total hemoglobin maps; -
No coding is required to go from raw data to results; -
Intuitive graphical user interface; -
Supports .snirf and BIDS formats; -
Has a visualization of the result graph.
Cortivision PHOTON CAP wireless portable near-infrared optical brain imaging system has a wide range of applications and important scientific research significance in the direction of human factors engineering, neuromanagement, neuroengineering management, human-computer interaction, human-computer-environmental systems engineering, environmental behavior, architectural design, and user experience.
Company Profile














































