Description
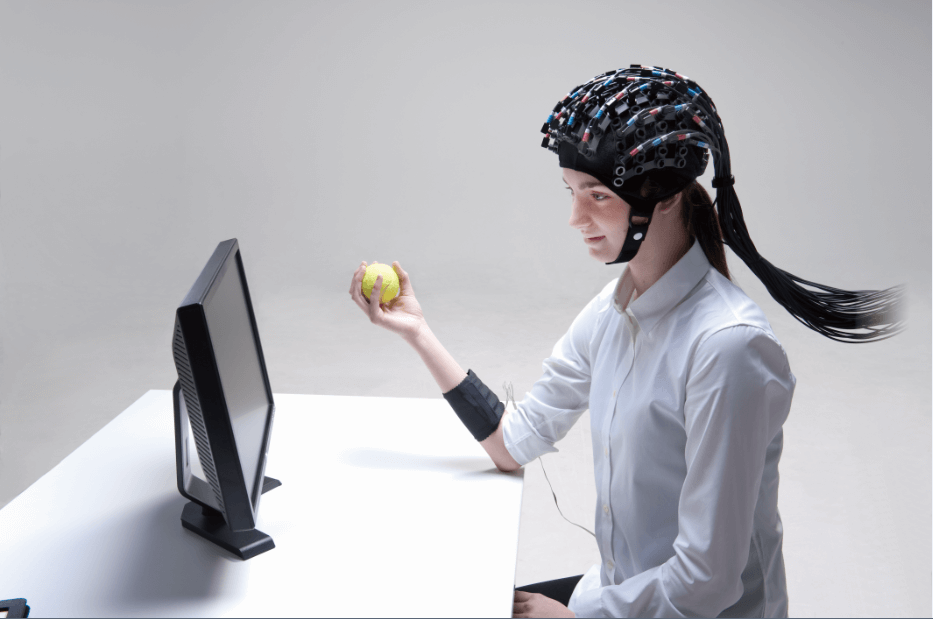
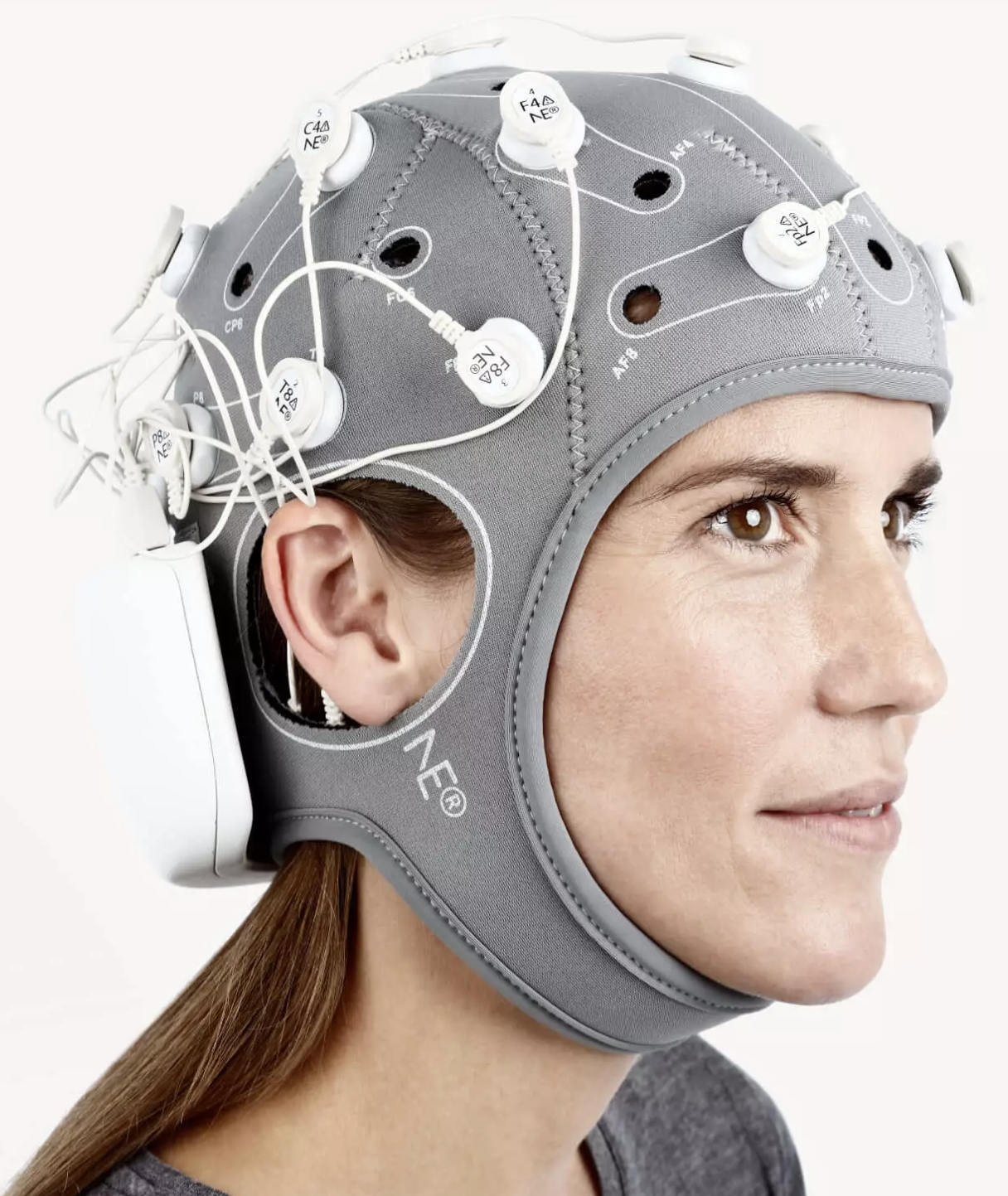
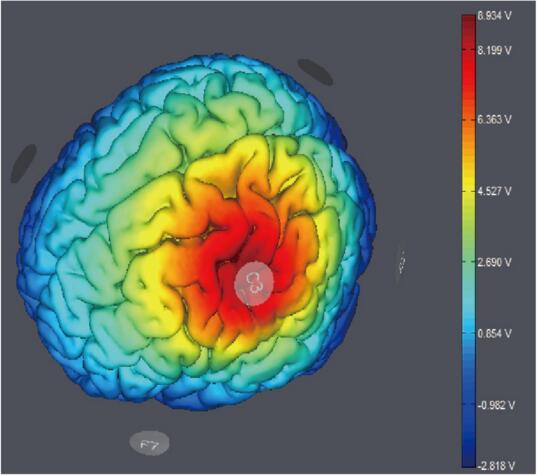
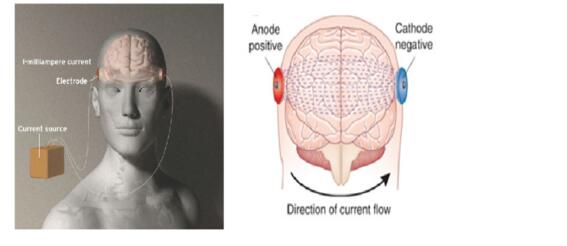
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)TDCS is a form of neurostimulation that uses a constant, low current delivered directly to the area of the brain of interest via small electrodes. When these electrodes are placed in the area of concern, the current induces current flow in the cerebral cortex, which can increase or decrease neuronal excitability in specific areas to alter brain functioning. |
   |
   |
Historcal review Historical review
|
Bipolar stimulation
|
   |
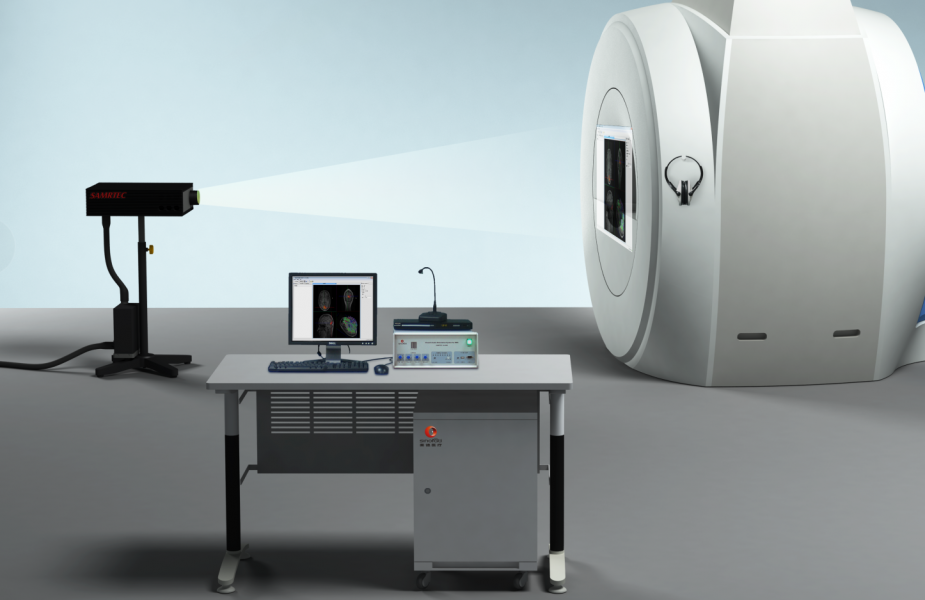
| 1. Non-invasive wireless transcranial electrical stimulator mainframe | ||
|
*1.1 Number of electrical stimulation channels.
*1.2 Transmission method.
*1.3 Transcranial electrical stimulation modalities.
1.4 Flow limitation.
1.5 Current accuracy.
1.6 Current accuracy.
1.7 Current stimulation rise and fall.
1.8 Impedance test.
1.9.1 Voltage.
1.9.2 tRNS Amount of stimulus change.
|
8 channels
Wireless Bluetooth Blue Tooth 2.1
tDCS transcranial direct current stimulation, tACS transcranial alternating current stimulation, tRNS transcranial random noise stimulation, Sham pseudo-stimulation and other modes
+/-2mA per electrode
<10% (<1% after calibration)
<1 μA microamp level
Adjustable time
Each of the 8 channels can be tested in real-time impedance
Reach +/-15V (maximum stimulation potential of 30V)
<640μA
|
|