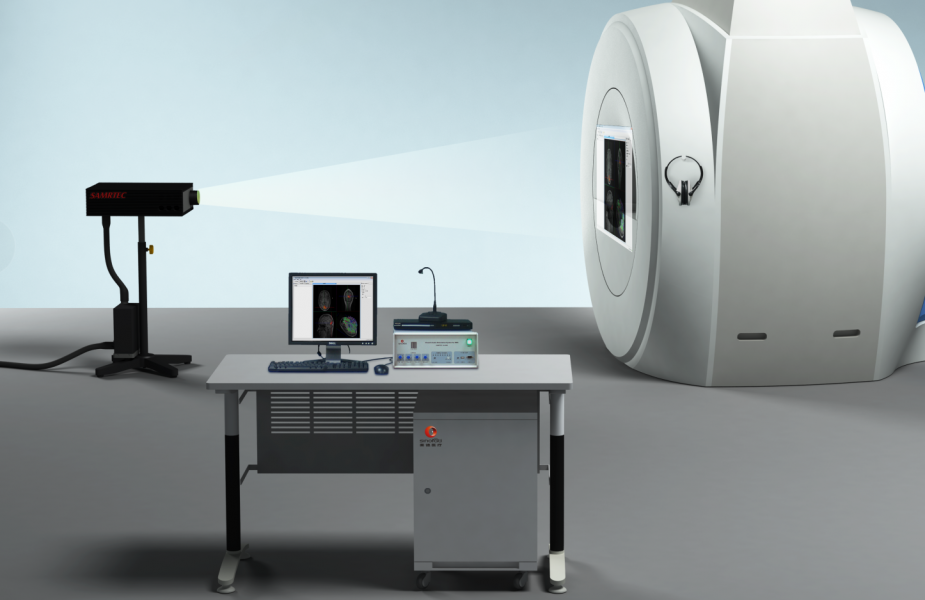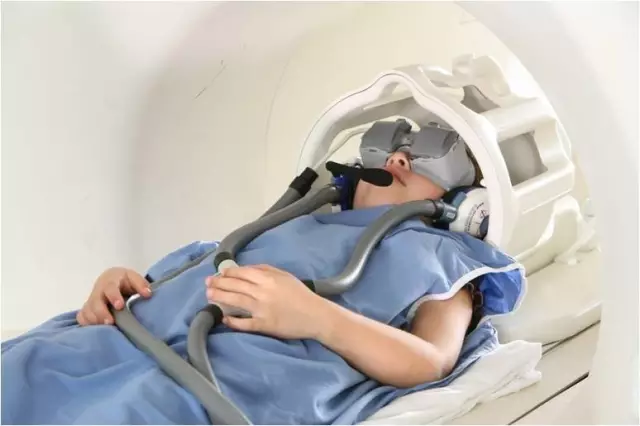

Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has developed into an important tool for studying brain function and has provided us with some new understanding of neurophysiology. Functional MRI experiments examine the brain activity of subjects as they perform a pre-determined task, generally in response to an external stimulus. Among them, visual stimuli have become the most important part of external stimuli in experiments and are used to study almost all brain functions.
Generally, the same stimuli are presented to both eyes in an experiment, however, in recent years a series of important experimental studies have required different stimuli to be presented to both eyes, such as studies of binocular antagonism, interocular information transfer, 3D depth perception, and studies of visual system damage (amblyopia, stereoacuity deficit, etc.). This places new demands on our NMR supporting experimental equipment. In order to achieve the effect of presenting different images to both eyes, there are two main methods to achieve this. There are two different classifications, the first one being the projection-mirror form and the eyepiece form depending on the stimulus presentation device. The projection-mirror format involves projecting an image onto a screen via a computer, with the subject lying supine inside the NMR machine and observing the stimulus through the reflection of the mirror. The eyepiece, on the other hand, is placed on the subject's head, within a fixed frame on the head. The second classification is based on the nature of the image display, one in which the two pictures are fused into a single picture and the subject passes through a spectral filter to achieve binocular split vision. The other is that the two images are presented to the subject independently, which removes the effects of crosstalk (through the eyepiece, Figure 1).
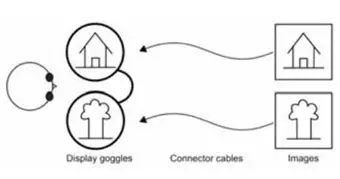

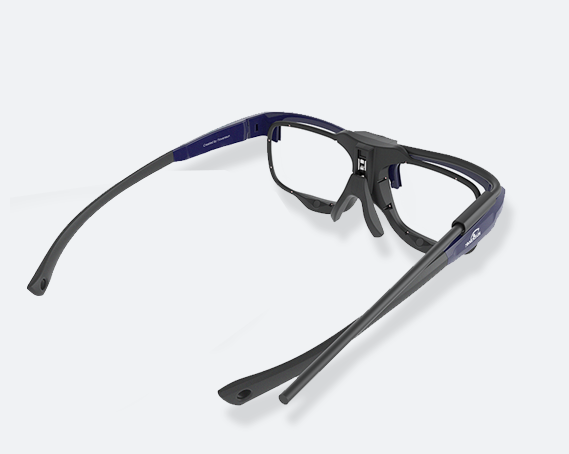
Figure 1. Eyepiece-based presentation of binocular split-vision stimuli
From the experimental results, the visual stimuli were presented using spectral filters (i.e., projector presentation), and the neutral density filters attenuated the brightness of the pictures. In addition, this approach is also very dependent on the angle at which the subject's head is placed, and even weak head movements can lead to larger light crosstalk between stimuli. Finally, this way of using spectral filters produces a sequential effect, so in order to balance the sequential effect in both eyes, different sequential repetitions must be performed, thus increasing the time of the experiment as well as the fatigue of the subject. The above problems can be effectively avoided by using the eyepiece format. Firstly, the eyepiece can make the two pictures presented independently, avoiding crosstalk of light. Secondly, the angle between the eyepiece and the subject's head is relatively fixed, and slight head movement will not cause the angle to change.
Resonance Technology, Inc. has been developing applications for functional MRI research for many years. The company has long been in close contact with higher education and research institutions around the world and involves its partners in every step of the development process - from the conceptualization of new product prototypes to testing. The company's goal is to become the standard in the field of MRI-compatible visual and auditory and subject-response devices, and the visual stimulation goggles included in RT's functional brain audiovisual stimulation systems are smaller and can be conveniently placed under the head panel, while having high resolution to ensure distortion-free image presentation. To date, many studies on binocular information transfer and visual deficits have been conducted using RT's visual stimulation goggles with good results [1][2][3].
In addition, Engström and his colleagues compared the effects of goggle and projector presentation in a visual stimulation study. It was found that visual stimuli presented through a projector did not activate the corresponding brain areas, whereas the use of a visual stimulus goggle activated the corresponding brain areas. Therefore, the study recommended the use of visual stimulation goggles [4].
RT's brain function audio-visual stimulation system is introduced by
The RT brain function audiovisual stimulator provides subjects with realistic visual and audio stimulation through its audiovisual stimulation equipment on the one hand, creating a virtual MRI comfort zone for subjects, helping to calm anxiety and minimize claustrophobia common in testing, and greatly enhancing the scanning experience for subjects. This reduces the test preparation time, increases the subject's concentration time and improves the subject's test efficiency. On the other hand, its visual stimulator (eyepiece) can be used to provide flexible visual stimulus presentation within the MR scanner, enabling 3D display and clear readability of stimulus information. The auditory stimulator (shielded headset) is a high-precision electronic earpiece for presenting auditory stimuli inside the MR scanner, which greatly reduces the noise inside the MR scanning chamber and ensures that the subject can hear the sound stimuli clearly. The high-sensitivity response panel allows for accurate recording of the subject's behavioral responses. It also enables simultaneous recording of behavioral responses and MR scans to explore the relationship between behavior and brain activity and to gain a deeper understanding of brain function. In addition, it can also be connected with the eye tracking system to collect the subject's eye movement information, providing more data information for understanding the subject's information processing process. Therefore, the brain function audio-visual stimulator can ensure the accuracy of fMRI research to the greatest extent, and the user can easily get started and master it, which greatly improves the research efficiency and is an important and indispensable part of fMRI research.
The system consists of the following main components.
◆Eyepiece or LCD screen to provide visual stimulation
◆ Headphones that provide auditory stimulation
◆ Controller host
◆ Remote switching controller
◆ Remote controller and intercom system
◆ Subject response input device
◆ Stimulation of compilation software and computers, etc.
◆ Optional MRI eye tracking system
RTThe company's functional brain audiovisual stimulation system features.
Eyepiece.Dual display stereo image playback enables 3D display and transmission of visual paradigms through the screen. With an advanced process of 500,000 pixels per 0.25 square feet of area, even very small text messages transmitted from a computer can be clearly readable. The eyepiece can be applied in all standard head coils with no effect on the signal-to-noise ratio and without interference from magnetic fields.
▼
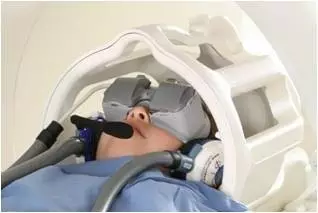

LCD screen.With a large 47-inch display, 1920 x 1080 resolution, full-screen HD 1080 P, contrast ratio of 4000000 : 1, support for 2D and 3D display.
▼


Auditory stimulation headphones:The system is a two-way subject intercom with an active noise-canceling microphone that reduces MRI noise by 30 dB, dual volume control - adjustable for both subject and technician, and transmission of audio signals from the console to the MRI suite via a dual fiber optic connection with laser communication.
▼
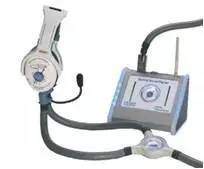

Subjects' response system.The easy-to-use subject response device is highly sensitive and allows for accurate recording of the subject's response.
▼