Part.1
introductory
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Since the 21st century, the demand for coal has climbed, surface coal reserves have been depleted, and deep coal mining has increased. However, the temperature and humidity of the underground environment have also risen, and the hazards posed by high temperatures and humidity are one of the most significant challenges to coal mining safety. It has been found that when mine temperatures exceed 28°C, the physiological health of miners is severely compromised, with a significant increase in the prevalence of certain diseases. In addition, every 1°C rise in temperature leads to aminersproductivity is reduced by 6-8%. when the ambient temperature exceeds 35°C, theminersThe operating efficiency is only 20% of normal conditions. when theminersHeat-induced fatigue can affect their ability to react quickly when they need to react to special situations.
In coal mine safety research, human safety behavior has been the focus of research, and alertness is closely related to safety behavior. Decreased cognitive abilities such as alertness can lead to fatigue, decreased work performance, the emergence of risky behaviors, and the occurrence of accidents. It is important to enhance the understanding ofminersThe management of safe behavior requires the study of the effects of the external environment on theminersneurocognitive functioning to gain insight into theminersmechanisms underlying unsafe behaviors. In order to fully understand theminersintrinsic mechanisms of insecure behavior, we will use fNIRS to evaluate 100minersAlertness levels under different temperature and humidity conditions.
Part.2
Method
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Subjects
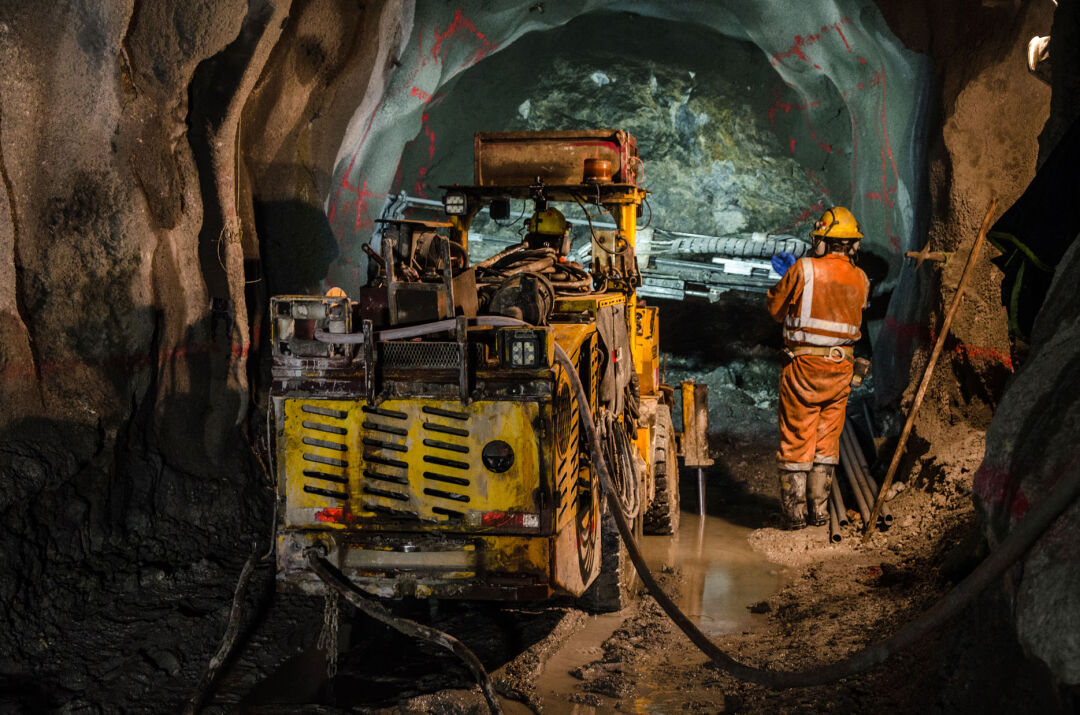
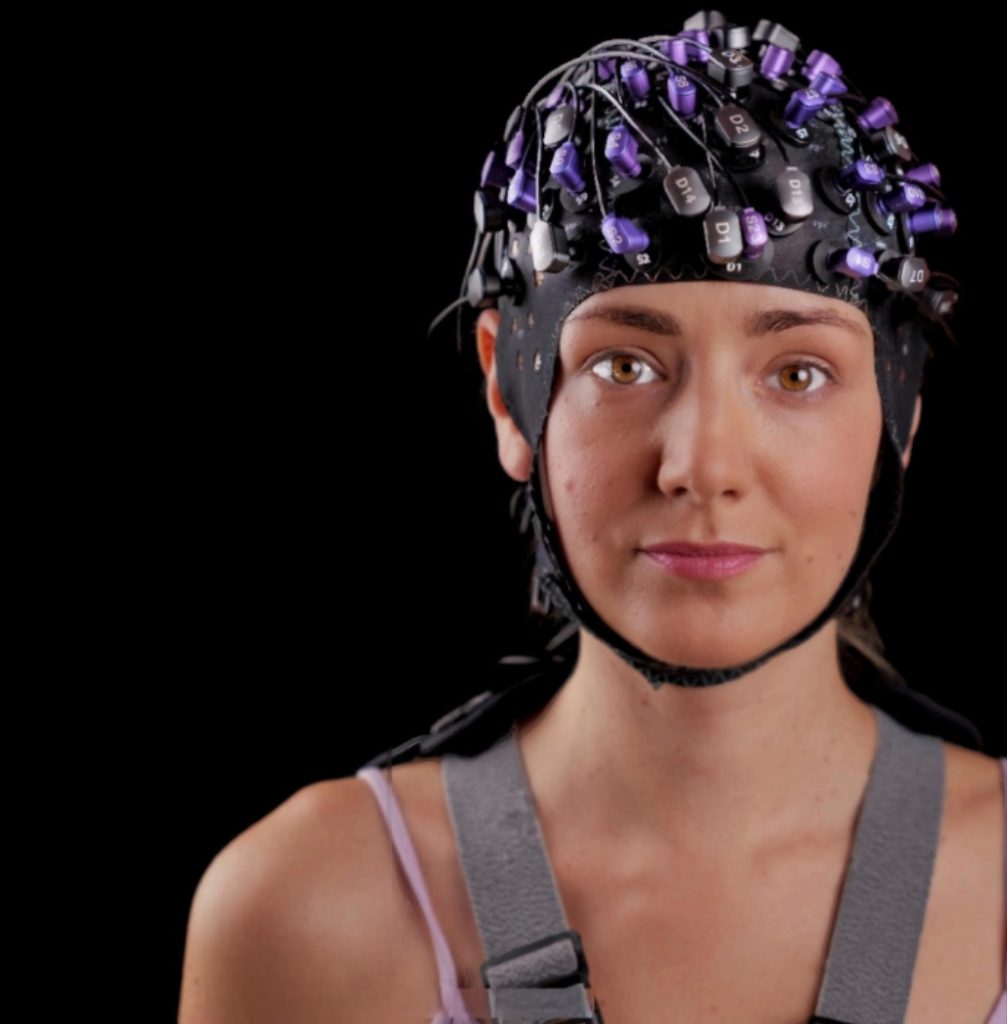
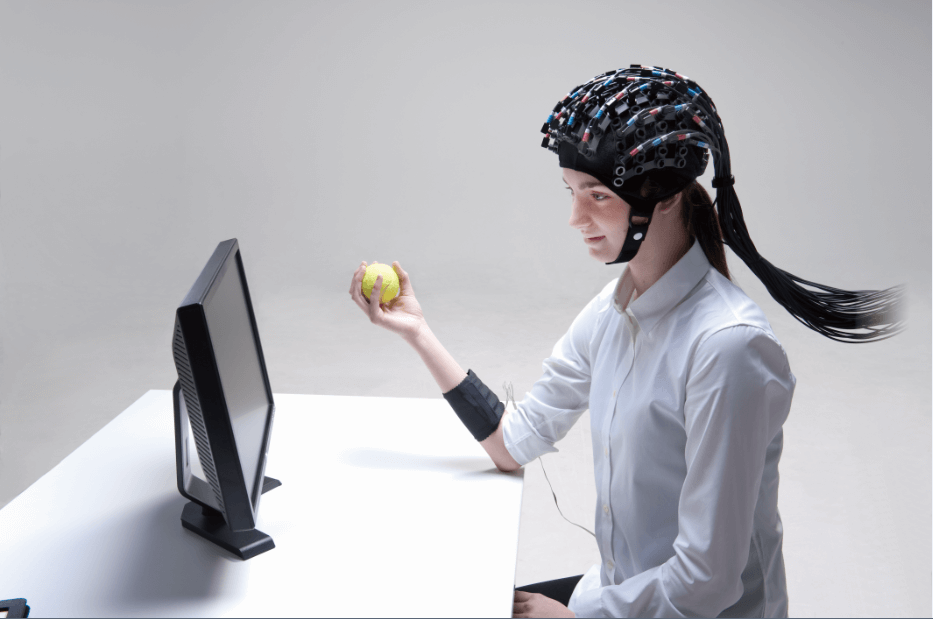
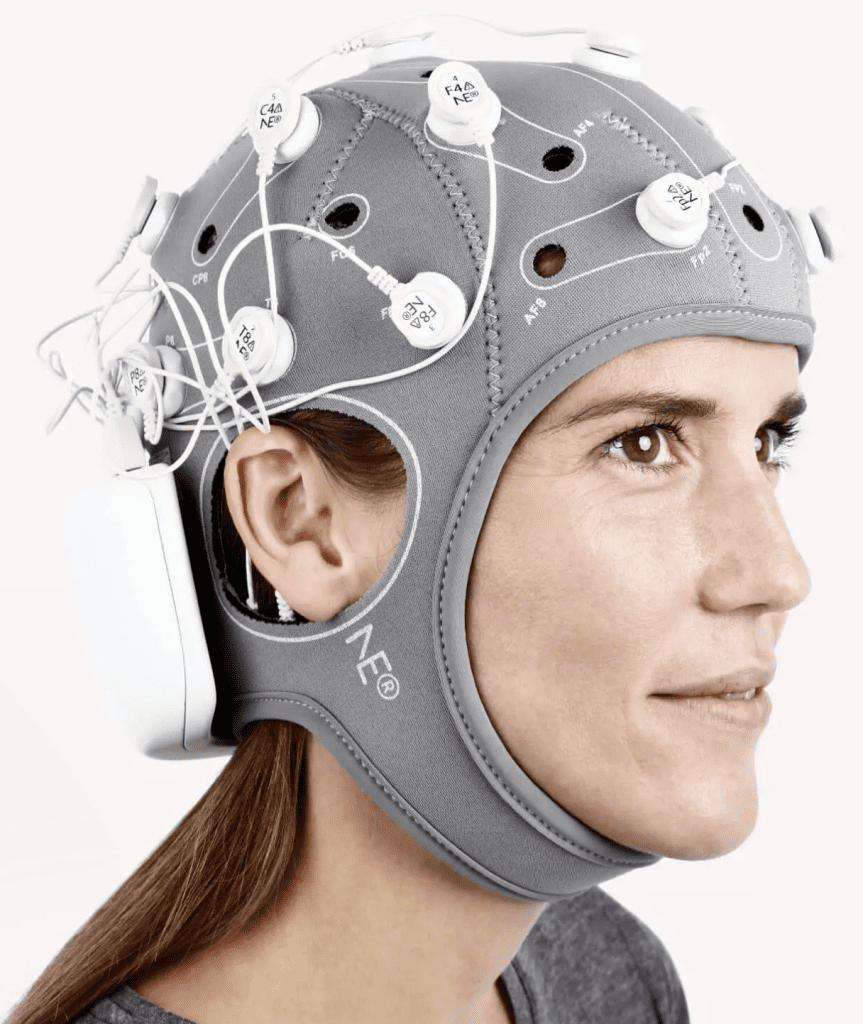
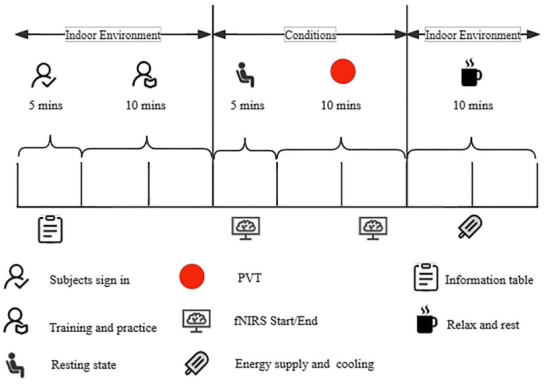
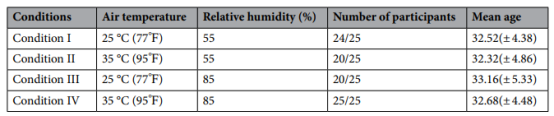
Recruitment of 100 healthy menminers(26-42 years old) were divided into 4 groups, all subjects were right-handed and had normal vision.The experimental environment was in a temperature and humidity chamber in the Safety and Emergency Management Laboratory of Xi'an University of Science and Technology (Fig. 1), and the subjects wore fNIRS (Cortivision Photon Cap) devices.Ten light sources and nine detectors in the device were selected and placed in the subjects' prefrontal lobes (PFC), creating a total of 27 channels (Figure 2).








Psychomotor Vigilance Task (PVT)
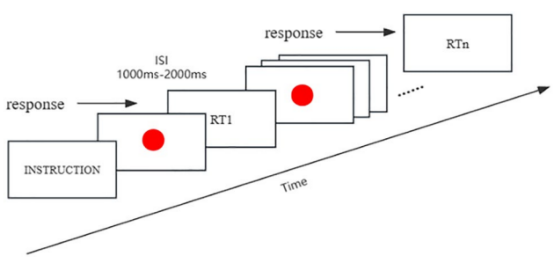
The PVT is a simple test task that assesses and measures the time required for subjects to respond to irregular stimuli when presented (Figure 3). In this task, subjects are required to attend to each stimulus and respond in time to the target stimulus when it is presented, recording reaction time (RT) and error rate (ER).


Part.3
Experimental design
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The present study used E-prime 3.0 to present PVT stimuli. During the task, subjects were required to respond promptly to randomly presented red dots. Since the hemodynamic response does not return to baseline levels until approximately 10 seconds after reaching peak, at least 10 seconds or more were spaced between each trial (Fig. 4).




Part.4
Results
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Behavioral outcomes
The results of the RT and ER analyses indicated that temperature change had a greater effect on subjects' cognitive performance on organizing than humidity. Increased temperature resulted in significant differences in RT and ER regardless of humidity conditions. In contrast, an increase in humidity only affected cognitive performance at high temperatures.
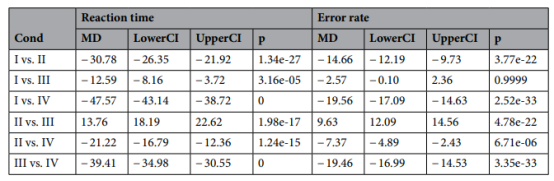


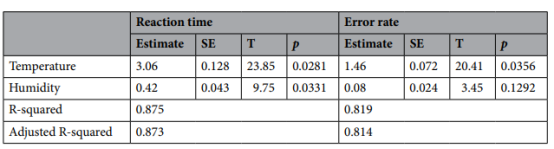
Temperature and humidity were used as independent variables and RT and ER as dependent variables in two separate multiple linear regression models. The results showed that temperature had a statistically significant effect on RT and humidity had a negative and significant effect on RT. For ER, temperature had a positive and significant effect on it, while humidity had no statistically significant effect on it.


Part.5
fNIRS results
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
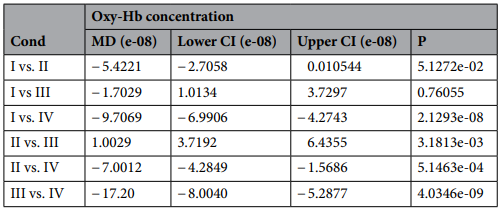
Tukey's HSD analysis of Oxyy-Hb concentration in all 19 channels under different conditions, from the table, it can be found that there is a significant change in Oxyy-Hb concentration by increasing temperature and humidity.


The analysis of ROI found that the effect of humidity on activated brain regions was not as significant as the effect of temperature. A Bonferronin correction was performed and found that there was significant activation in all four conditions in ROI B. However, in the activation map it can be found that temperature had a greater effect on activation in ROI B. The overall level of activation in ROI B was lower than that in ROI A. The activation level in ROI B was lower than that in ROI A. The activation level in ROI B was lower than that in ROI A.
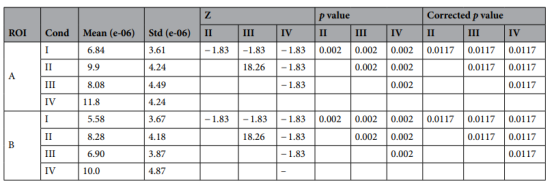


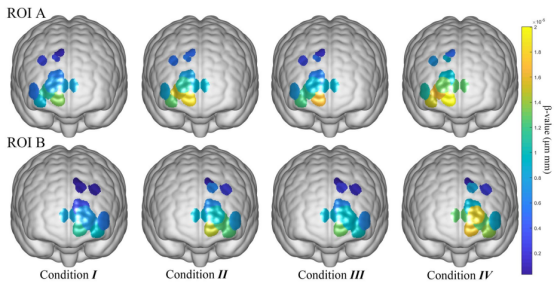


Visualization of hemodynamic response under different conditions showed significant differences in response time, peak time, peak amplitude, and recovery time between the right (ROI A) and left (ROI B) regions. These results show a clear differential response pattern of the bilateral PFC, with the right PFC exhibiting higher sensitivity and slower recovery under unfavorable conditions, in contrast to the faster, more stable response observed in the left PFC.
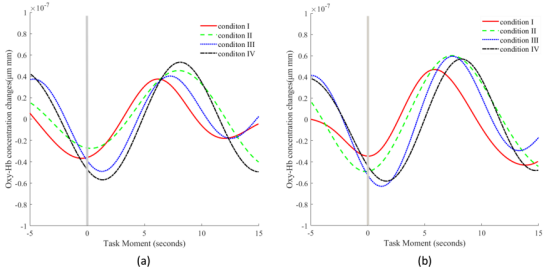


Fig. 6 Oxy-Hb time trends, mean ROI values for all subjects across conditions, gray is stimulus onset (a) ROI A (b) ROI B
Part.6
Conclusion
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In this study, fNIRS was used to investigate the effects of temperature and humidity variations during the PVT mission on theminersEffect of alertness level. It was found that the cognitive load of the subjects increased significantly due to the increase in temperature and humidity, mainly in the form of longer reaction time, increased error rate and blood oxygen concentration. In addition, temperature had a greater effect on these outcome metrics than humidity. In the ROI results, the level of activation in the channel also increased with elevated temperature and humidity, especially more pronounced in response to the right PFC. In future studies, the fNIRS technology application could be used to study different environmental conditions in theminersChanges in functional connectivity and local efficiency in the brain.
Part.7
quote
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Tian, C., Li, H., Tian, S. et al. The neurocognitive mechanism linking temperature and humidity with miners' alertness: an fNIRS study. sci Rep 14, 11796 (2024). Sci Rep 14, 11796 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-62674-z
Part.8
Cortivision Wireless Portable Near Infrared Optical Brain Imaging System
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()



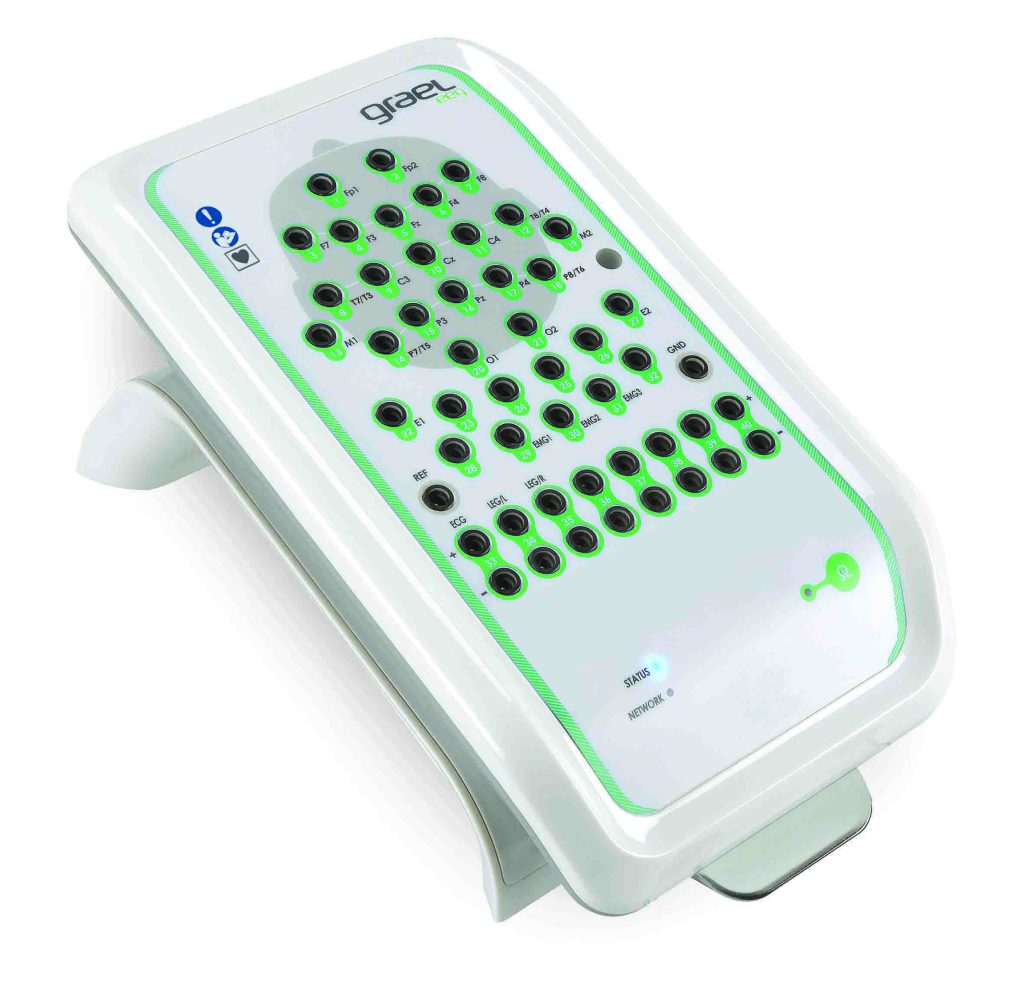
The PHOTON CAP device developed by Cortivision is a wireless portable near-infrared brain optical brain imaging system (fNIRS), which is a device that can effectively measure changes in the concentration of hemoglobin in the brain. The device records and analyzes changes in oxyhemoglobin concentration and deoxyhemoglobin concentration in active brain regions during the perception of external stimuli, and speculates on the interrelationships between perceptually active brain regions and their associated brain regions.
The Cortivision PHOTON CAP is a 37-channel device consisting of 16 transmitters (including 4 shortwave transmitters), 10 detectors. The device is wireless, portable, lightweight, safe and highly compatible, and can be used in conjunction with a wide range of devices such as VR, EEG/ERP, oculomotor, and physiological multidetector.





-
Real-time fNIRS and IMU raw data, oxyhemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin, and total hemoglobin maps; -
No coding is required to go from raw data to results; -
Intuitive graphical user interface; -
Supports .snirf and BIDS formats; -
Has a visualization of the result graph.
Cortivision PHOTON CAP wireless portable near-infrared optical brain imaging system has a wide range of applications and important scientific research significance in the direction of human factors engineering, neuromanagement, neuroengineering management, human-computer interaction, human-computer-environmental systems engineering, environmental behavior, architectural design, and user experience.
Company Profile
Ltd, invested by Zhongke (Guangdong) Science Group and relying on Guangdong Human Factors Technology Research Institute and Wuhan Human Factors Engineering Technology Research Institute, is a new type of high-tech enterprise based on the direction of psychological human factors, driving human factors, biomechanics, user experience, virtual reality and other directions, integrating production, research and development, sales and technical services, and has been selected as a national high-tech enterprises, science and technology-based Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) and Zhongguancun High-tech Enterprises.



Hengzhi Technology independently researches and develops driving human factors system, virtual reality graphical editing software, light environment psychological assessment system, psychological and human factors experimental teaching system, and at the same time as the general agent of Poland Cortivision near infrared, Russia Mitsar electroencephalography and Germany Eyelogic eye-tracking instrument in China, and the general agent of biomechanics and gait analysis scientific research products such as surface electromyography of Italy BTS, and so on. AdHawk Mindlink (Canada), QuaeroSys (Germany), Noldus (Holland), Tobii (Sweden), MindMedia (Holland), Biopac (U.S.A.), ETT (U.S.A.), and other products in the field of olfactory/gustatory stimulation. We have served Tsinghua University, Peking University, Beijing Normal University, Northeast Normal University, Yanshan University, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, Shenzhen University of Technology, Xi'an University of Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Xinjiang Normal University, Qiyuan Laboratory, China Electronics Technology Group 27, China Electronics Technology Group 28, Huawei Technology, InkScan, NetEase, Aerospace Academy II, and so on. Thousands of colleges and universities, research institutes and enterprises and institutions continue to carry out in-depth cooperation in talent cultivation, production and research cooperation, and transformation of achievements.