Research Background










As the world's largest coal producing country, China's coal mine safety is a matter of economic development and social stability. Despite the continuous upgrading of technology and equipment, the unsafe behavior of miners is still the main cause of accidents (accounting for more than 70% of the causal factors of accidents). Traditional management focuses on external supervision, but neglects the internal psychological mechanisms of individuals.
the main body of a bookPresenting a fresh perspectiveassume (office)Personality traits drive risky decisions.By integrating neuroscience (fNIRS technology) and psychology experiments, it reveals for the first time how the five major personalities of miners influence safety behavior through brain activities, providing a scientific basis for precise safety management.




Research Methodology







The study adopted a multimodal experimental design, combining behavioral tasks, brain imaging and psychological assessment to construct a three-layer personality-behavioral-neurological association model.
Experimental tools
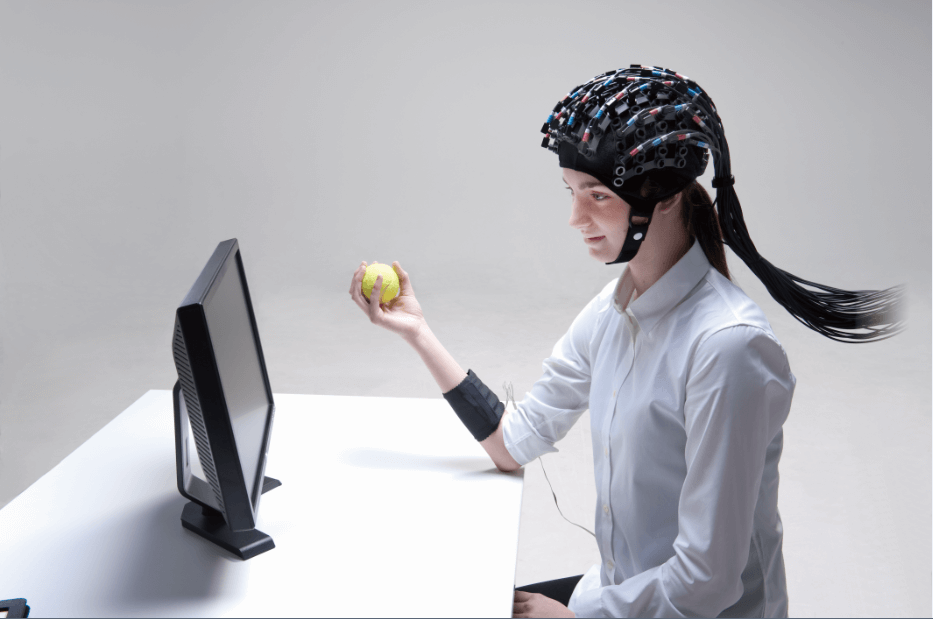
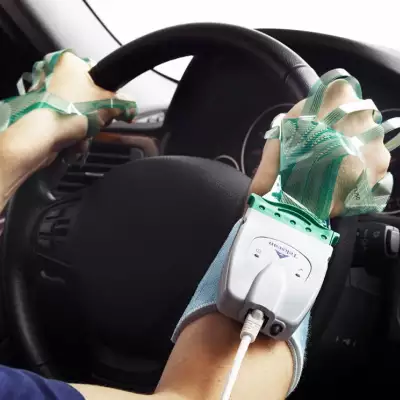
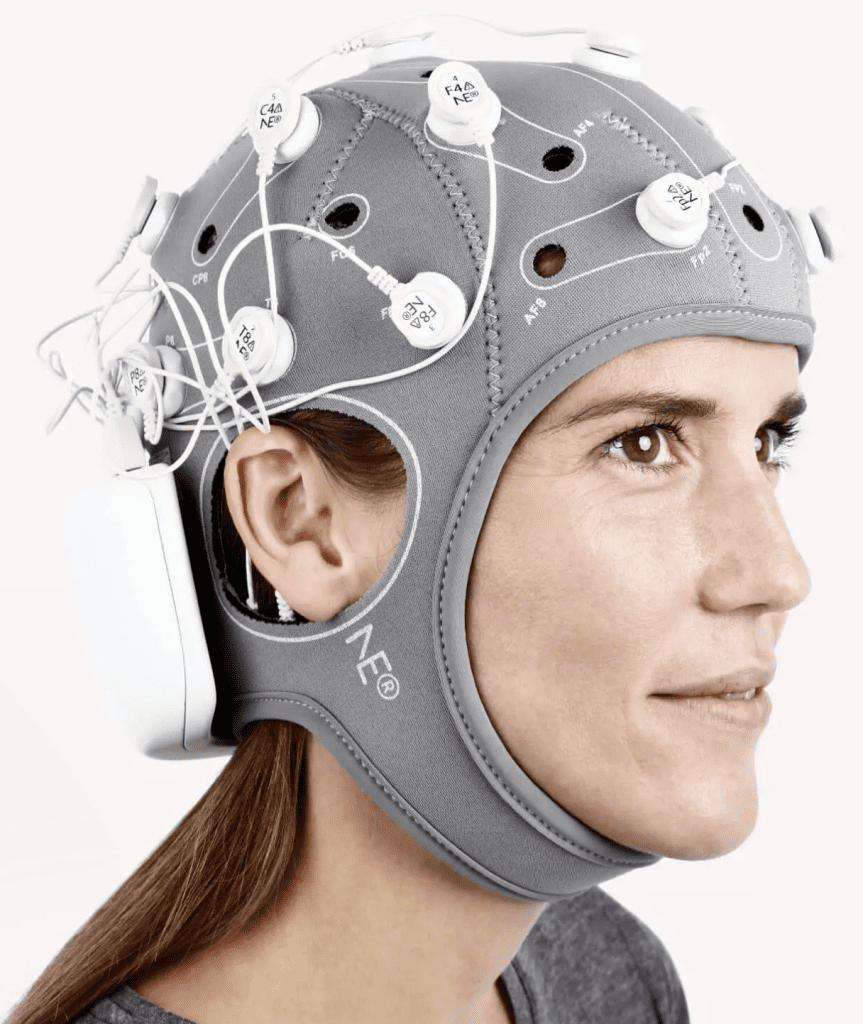
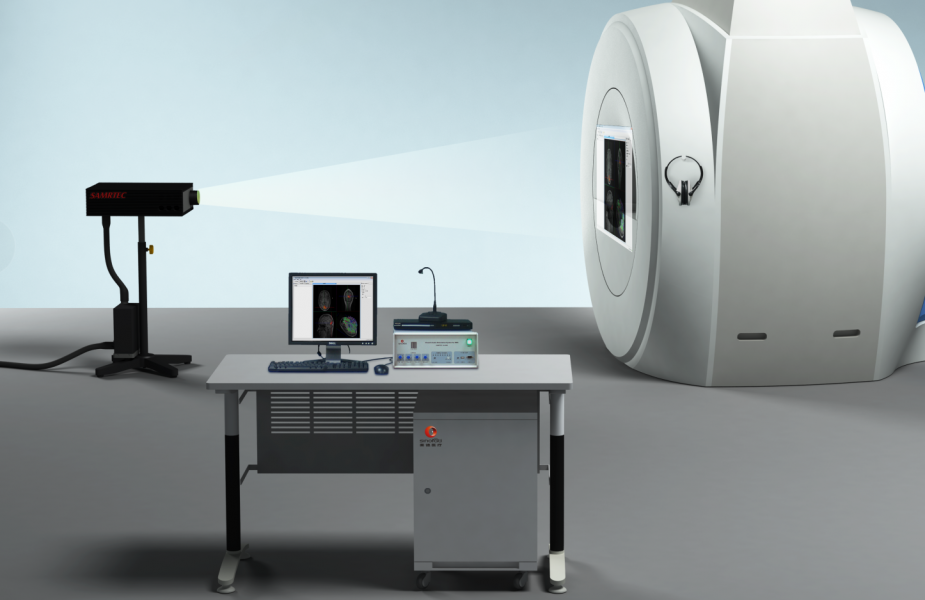
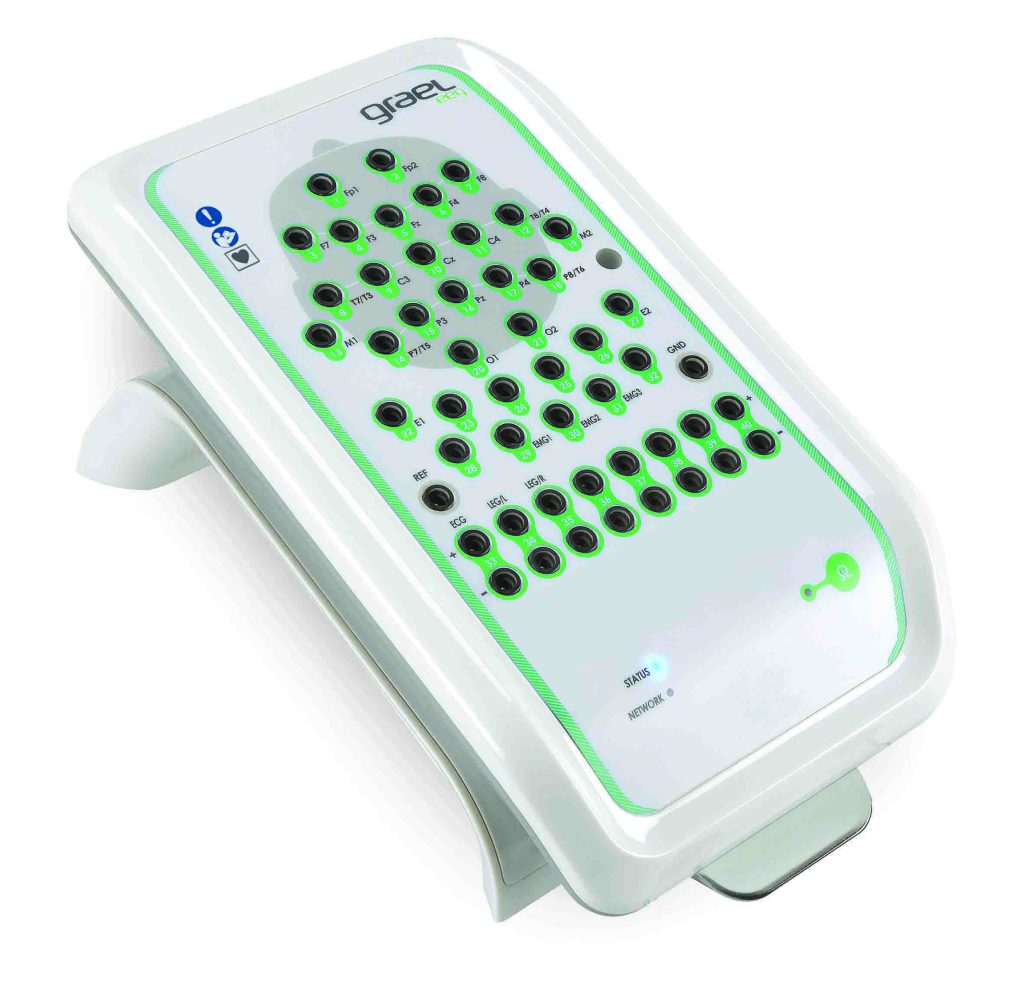
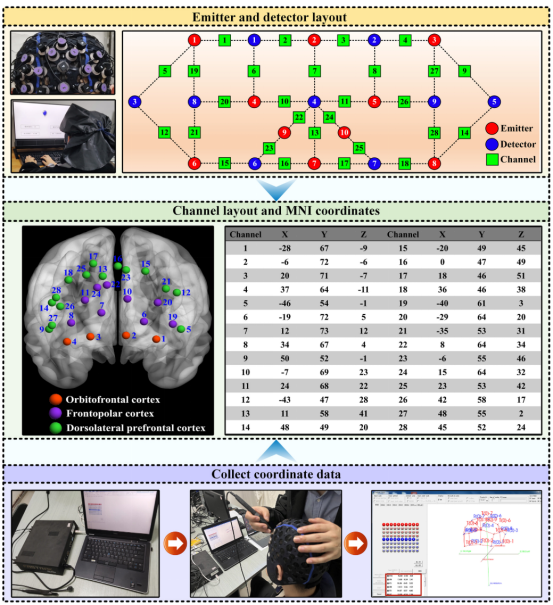
1. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) Equipment:
pluckOxyhemoglobin (HbO) concentration and brain area activation levels (beta values) were monitored in real time with a Cortivision PHOTON CAP portable device covering 28 channels in the prefrontal lobe.


2. Behavioral experimentation paradigm:
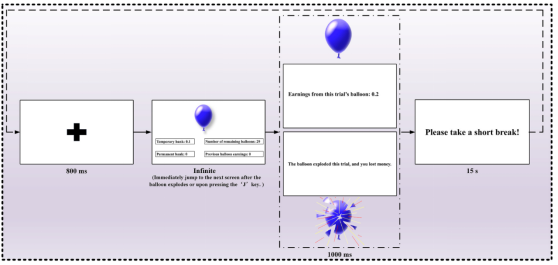
Balloon Analog Risk Tasks (BART): Programmed by E-Prime software to simulate miners' "risk-benefit" trade-off scenarios (e.g., whether to continue operations if equipment is abnormal), and to record the risk propensity (the average number of times an unexploded balloon is inflated).
3. Psychological assessment tools: The
Chinese version of the Big Five Inventory (BFI-2): a 60-item, 5-point scale assessing openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and negativity.suffix forming noun from adjective, corresponding -ness or -ity.
experimental condition
The study set up two types of core experimental conditions focusing on the association between personality traits and risky decision making:
1. High Risk Scenario Group:
The BART task simulates the gradual accumulation of risk (e.g., a balloon expanding to an explosion) and corresponds to the daily decisions of miners who face a "latent risk of non-explosion".
2. Feedback sensitivity group:
Positive feedback: subsequent risk propensity (PBART score) after task success (balloon did not explode).
Negative feedback: subsequent risk propensity (NBART score) after task failure (balloon explosion).
data acquisition
1. Neural Data:
Changes in HbO concentration in prefrontal 28 channels (Homer3 software processing) and activation intensity in brain regions (NIRS-KIT analysis).
2. Behavioral data:
Risk propensity score, positive/negative feedback sensitivity in BART tasks.
3. Psychological data:
Five personality dimension scores for group comparisons (high/low openness, due diligence, etc.).
participants
54 male miners (age 28.98 ± 2.67 years) covering positions such as coal mining machine operators and hydraulic support workers.
experimental procedure
1. Baseline Measurement:
Complete the BFI-2 questionnaire and categorize into high/low groups by personality dimension (e.g., high extraversion vs. low extraversion).
2. Mission training:
5 BART pre-labs to familiarize with operational procedures.
3. Formal experiment:
30 BART tasks with simultaneous acquisition of fNIRS cerebral blood oxygenation signals and behavioral data.
4. Data integration:
Matching behavioral data (risky decision making) with neural activity (prefrontal activation patterns) to analyze the neural mechanisms of personality traits.

Experimental design
1. Comparison between groups:
Cross-sectional study design comparing high/low personality groups on risk propensity, brain region activation.
2. Variable control:
-Fixed balloon blast point means (6 times) to avoid learning effect interference.
-Use Benjamini-Hochberg correction (FDR) to reduce statistical false positives.
Collected data
1. Behavioral data:
BART score, positive/negative feedback sensitivity.
2. Neural data:
HbO concentration, activation strength (beta value) of prefrontal 28 channels.
3. Psychological data:
Five personality dimension scores.




Study results







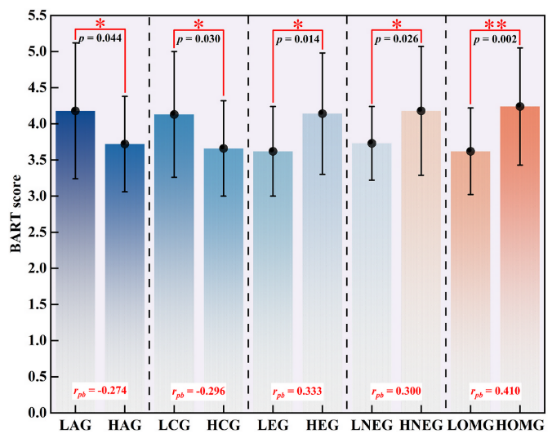
1. Personality traits determine risk propensity
-High risk group:Extraversion, Openness, and Negative Emotionality miners had significantly higher BART scores.
-Low risk group:Desirability, due diligence miners are more cautious and especially concerned about negative feedback (e.g., accident warnings).


2. Activation of brain regions reveals decision-making mechanisms
-DLPFC (dorsolateral prefrontal):Higher extroversion miners activate more strongly, reflecting a balanced treatment of positive/negative feedback.
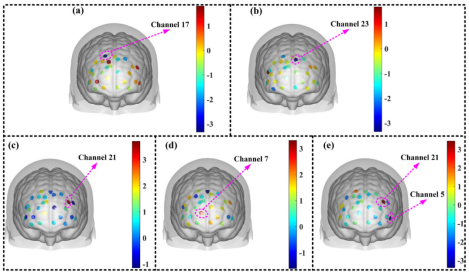

-OFC (orbitofrontal cortex):High negative emotionality miners fluctuated significantly and emotional stress drove risk-taking (Channel 25 HbO concentration difference p
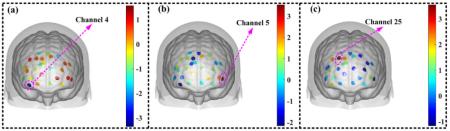


-FPC (Frontal Polar Cortex):High due diligence miner activation stabilizes and reflects systemic risk assessment capabilities.
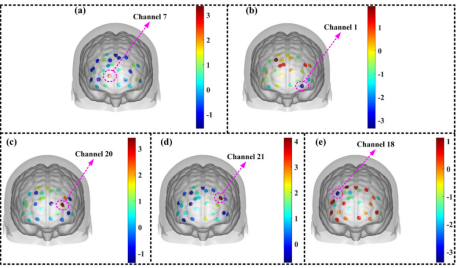


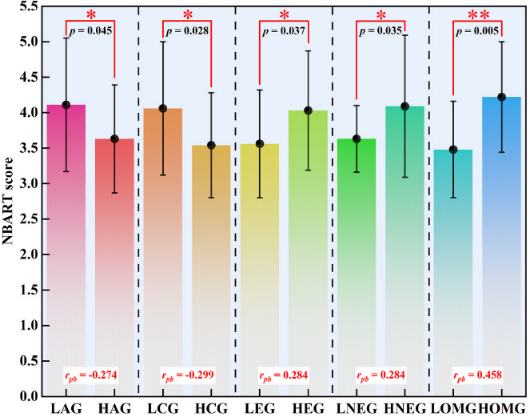
3. Differences in risk feedback sensitivity
-Extroverts:Stronger motivated by positive feedback (e.g., task success) (PBART score)ascend).
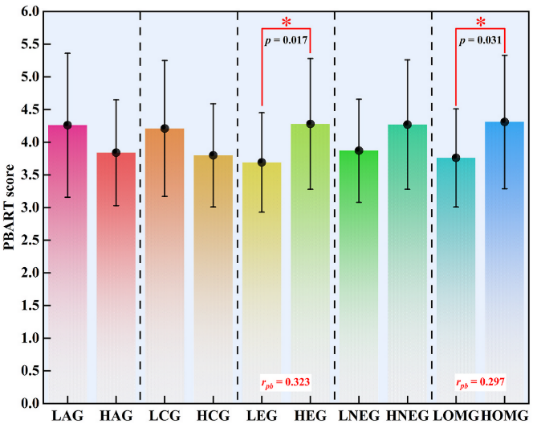

-Openers:Focusing more on the deeper causes of negative feedback (elevated NBART scores) reflects learning ability.


talk over







1.Why Personality Affects Safety Behavior: The
-Extroversion:Seek excitement and new experiences, and view risk as a "challenge" rather than a threat.
-Diligence:Enhance self-control and responsibility and inhibit impulsive decision-making.
-Negative emotionality:Stress triggers "emotional risk-taking" and requires psychological intervention.
2.Scientific significance of neural mechanisms: The
- DLPFCAs a "rational decision center", the activation strength is directly related to the fineness of the risk calculation.
- OFCfluctuations suggest the critical role of emotion regulation in safety management.
Findings







1. Miners' risk propensity can be accurately predicted by five major personality traits, with extroversion, openness and negative emotionality signaling high risk.
2. Prefrontal neural activity provides biomarkers for risky decision-making, such as abnormal fluctuations in Channel 25 (OFC) that warn of emotional risk-taking.
3. Integration of personality assessment and neuromonitoring allows for individual-team optimization of security at a two-tiered level.
References:Mao J, Tian S, Tian F, et al. The relationship between coal miners' Big Five personality traits and risk propensity: Evidence from fNIRS[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2025, 107: 103750.
If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal!
Company Profile



Ltd. is an innovative high-tech enterprise focusing on cutting-edge technology, specializing in brain science, neural management, human factors engineering, biomechanics, anthropomorphic environments and XR simulation reality and other multidisciplinary cross-cutting fields. The company is invested by Zhongke (Guangdong) Science Group, relying on the scientific research strength of Guangdong Human Factors Technology Research Institute and Wuhan Human Factors Engineering Technology Research Institute, and has constructed a professional operation system integrating research and development, production, sales and technical service to provide customers with one-stop, high-quality scientific and technological solutions.
With excellent innovation ability, Hengbest Technology has been awarded many invention patents, software copyrights and registered trademarks, selected in many authoritative lists such as National High-tech Enterprises, and participated in the compilation of national standards and group standards. The company has been serving universities and research institutes for a long time, and has cooperated deeply with many national societies such as the Chinese Society of Ergonomics, the Chinese Psychological Society, the Architectural Society of China, etc. The company organizes and participates in more than 40 academic conferences every year to promote technical exchanges and the development of the industry.
With the concept of "Technology Empowerment, Innovation Drive", Hengzhi Technology is committed to become a leading technology enterprise in the industry, to help national scientific and technological progress and social development, and to work together with partners from all walks of life to achieve a better future of technological empowerment.



Scan the code to follow us